A merge sort is a O(n log n) sorting algorithm. I show in this example how to implement a merge sort in c++ using recursion. This algorithm is a divide & conquer based algorithm.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 | /***************************************************************************** * Merge Sort has O(nlogn) compute time. Splits the list into two sublists then * merges them back together sorting them *****************************************************************************/ void mergeSort(list<int> &myList) { list<int> listOne; list<int> listTwo; bool sorted = false; while (!sorted) { split(myList, listOne, listTwo); if (listTwo.size() == 0) sorted = true; merge(myList, listOne, listTwo); } return; } /***************************************************************************** * Splits a list into 2 lists *****************************************************************************/ void split(list<int> &myList, list<int> &listOne, list<int> &listTwo) { listOne.resize(0); listTwo.resize(0); //While not at end of list list<int>::iterator it = myList.begin(); while (it != myList.end()) { int lastItem = 0; while (it != myList.end() && *it >= lastItem) { listOne.push_back(*it); lastItem = *it; it++; } lastItem = 0; while (it != myList.end() && *it >= lastItem) { listTwo.push_back(*it); lastItem = *it; it++; } } return; } /***************************************************************************** * Merges 2 lists taking the smaller number each time from both lists. Then * copies the remaining numbers over if there are any left *****************************************************************************/ void merge(list<int> &merged, list<int> &listOne, list<int> &listTwo) { merged.resize(0); list<int>::iterator itOne = listOne.begin(); list<int>::iterator itTwo = listTwo.begin(); while (itOne != listOne.end() || itTwo != listTwo.end()) { if (*itOne < *itTwo) { merged.push_back(*itOne); itOne++; } else { merged.push_back(*itTwo); itTwo++; } } //Reached end of list One if (itOne == listOne.end()) while (itTwo != listTwo.end()) { merged.push_back(*itTwo); itTwo++; } else //Reached end of list Two while (itOne != listOne.end()) { merged.push_back(*itOne); itOne++; } return; } |
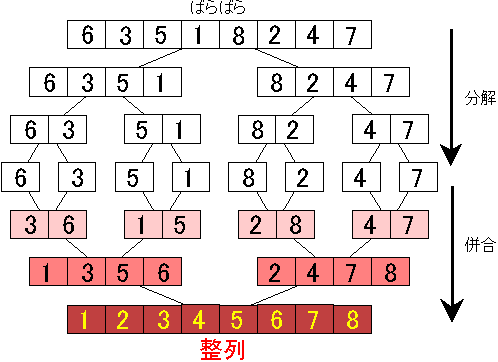
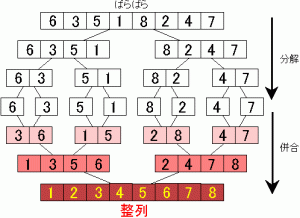
Merge Sort Algorithm:
- Divide the unsorted list into n sublists until each list contains 1 element. If the list has 1 element it is sorted!
- Repeatedly merge the sublists to produce new sublists until there is only 1 sublist remaining. The final list will be sorted!